Title: A phosphatidic acid-binding lncRNA SNHG9 facilitates LATS1 liquid–liquid phase separation to promote oncogenic YAP signaling
Rui-Hua Li, Tian Tian, Qi-Wei Ge, Xin-Yu He, Cheng-Yu Shi, Jun-Hong Li, Zhen Zhang, Fang-Zhou Liu, Ling-Jie Sang, Zuo-Zhen Yang, Ya-Zhuo Liu, Yan Xiong, Qingfeng Yan, Xu Li, Huai-Qiang Ju, Jian Liu, Liang-Jing Wang, Jian-Zhong Shao, Wenqi Wang, Tianhua Zhou & Aifu Lin
Abstract
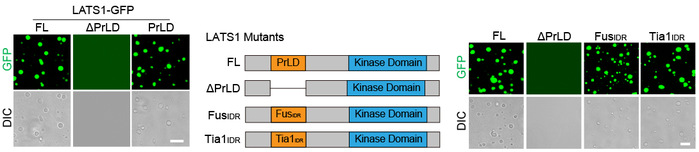
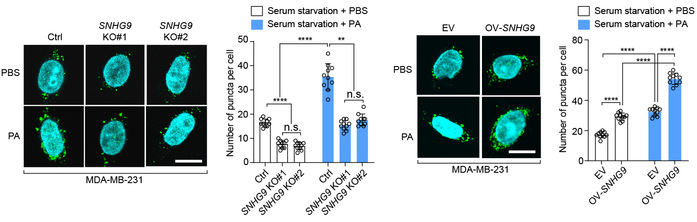
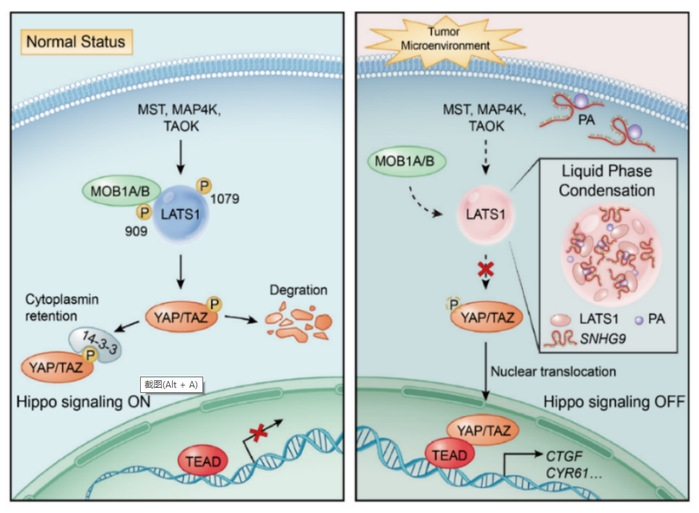
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are emerging as a new class of important regulators of signal transduction in tissue homeostasis and cancer development. Liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) occurs in a wide range of biological processes, while its role in signal transduction remains largely undeciphered. In this study, we uncovered a lipid-associated lncRNA, small nucleolar RNA host gene 9 (SNHG9) as a tumor-promoting lncRNA driving liquid droplet formation of Large Tumor Suppressor Kinase 1 (LATS1) and inhibiting the Hippo pathway. Mechanistically, SNHG9 and its associated phosphatidic acids (PA) interact with the C-terminal domain of LATS1, promoting LATS1 phase separation and inhibiting LATS1-mediated YAP phosphorylation. Loss of SNHG9 suppresses xenograft breast tumor growth. Clinically, expression of SNHG9 positively correlates with YAP activity and breast cancer progression. Taken together, our results uncover a novel regulatory role of a tumor-promoting lncRNA (i.e., SNHG9) in signal transduction and cancer development by facilitating the LLPS of a signaling kinase (i.e., LATS1).
Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41422-021-00530-9
More: Scientists discover role of lncRNA in regulating Hippo signaling via phase separation