Title: O-GlcNAcylation regulates epidermal growth factor receptor intracellular trafficking and signaling
Liming Wu, Yaxian Cheng, Didi Geng, Zhiya Fan, Bingyi Lin, Qiang Zhu, Jingchao Li, Weijie Qin, and Wen Yi
March 3, 2022 | 119 (10) e2107453119 | https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2107453119
Abstract
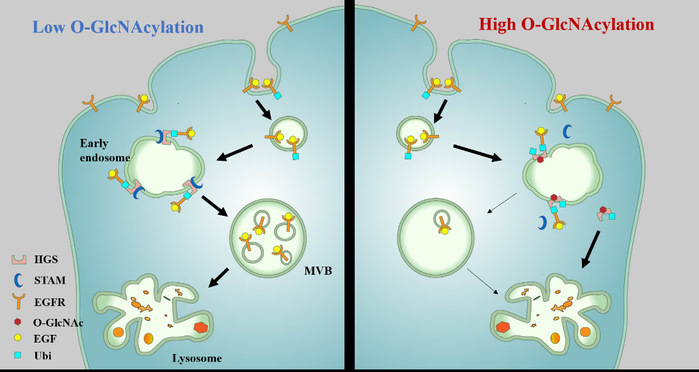
Ligand-stimulated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling plays fundamental roles in normal cell physiology, such as cell growth, cell proliferation, and cell survival. Deregulation of EGFR signaling contributes to the development and progression of diseases including cancer. Despite its essential role in biology, the mechanisms by which EGFR signaling is regulated in cells are still poorly understood. Here, we demonstrate that O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) modification serves as an important regulator of EGFR intracellular trafficking and degradation. Mechanistically, O-GlcNAcylation of hepatocyte growth factor regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HGS), a key protein in EGFR intraluminal sorting pathway, inhibits HGS interaction with signal-transducing adaptor molecule (STAM), thereby impairing the formation of endosomal sorting complex required for transport-0 (ESCRT-0). Moreover, O-GlcNAcylation increases HGS ubiquitination and decreases its protein stability in cells. Consequently, HGS O-GlcNAcylation inhibits EGFR intraluminal sorting and lysosomal degradation, leading to the accumulation of EGFR and prolonged EGFR signaling in cells. Furthermore, HGS glycosylation is demonstrated to promote tumor growth in the xenograft study and chemoresistance in liver carcinoma cells. Thus, our study reveals a role of O-GlcNAcylation in regulating receptor tyrosine kinase endocytic trafficking and signaling.
Link: https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2107453119