Title: O-GlcNAcylation promotes tumor immune evasion by inhibiting PD-L1 lysosomal degradation
Qiang Zhu, Hongxing Wang, Siyuan Chai, Liang Xu, Bingyi Lin, Wen Yi, and Liming Wu
Abstract
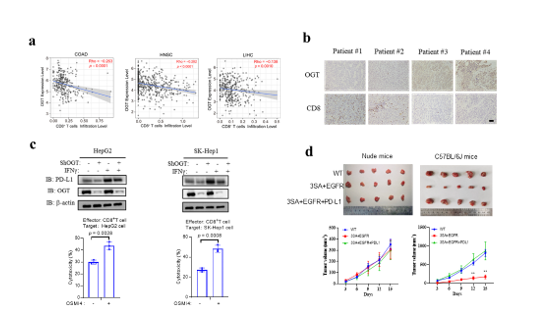
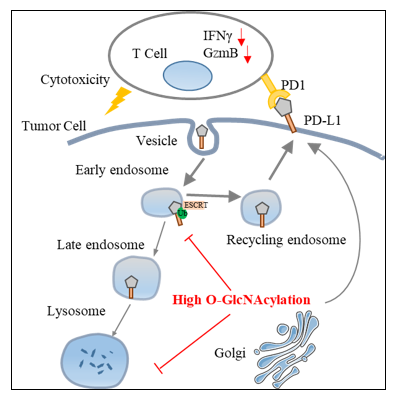
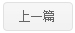
Programmed-death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and its receptor programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) mediate T cell–dependent immunity against tumors. The abundance of cell surface PD-L1 is a key determinant of the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade therapy targeting PD-L1. However, the regulation of cell surface PD-L1 is still poorly understood. Here, we show that lysosomal degradation of PD-L1 is regulated by O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) during the intracellular trafficking pathway. O-GlcNAc modifies the hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HGS), a key component of the endosomal sorting machinery, and subsequently inhibits its interaction with intracellular PD-L1, leading to impaired lysosomal degradation of PD-L1. O-GlcNAc inhibition activates T cell–mediated antitumor immunity in vitro and in immune-competent mice in a manner dependent on HGS glycosylation. Combination of O-GlcNAc inhibition with PD-L1 antibody synergistically promotes antitumor immune response. We also designed a competitive peptide inhibitor of HGS glycosylation that decreases PD-L1 expression and enhances T cell–mediated immunity against tumor cells. Collectively, our study reveals a link between O-GlcNAc and tumor immune evasion, and suggests strategies for improving PD-L1-mediated immune checkpoint blockade therapy.
Link: www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2216796120