Title: PD-L1-Targeting Biomimetic Photoresponsive Thermosensitive Liposomes for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Manman Tan, Chengyu Shi, Guangyi Chi, Xinwan Su, Fangzhou Liu, Linyu Zhu, Guangqian Cheng, Xiangyi Chen, Meng Yu, Yijian Chen, Ying Wang, Yu Chen, ShuLing Yan, Wenfei Wu, Qingfeng Yan, Jianzhong Shao, Kai Wang, Xiangrui Liu, Min Zhou, Aifu Lin
Abstract
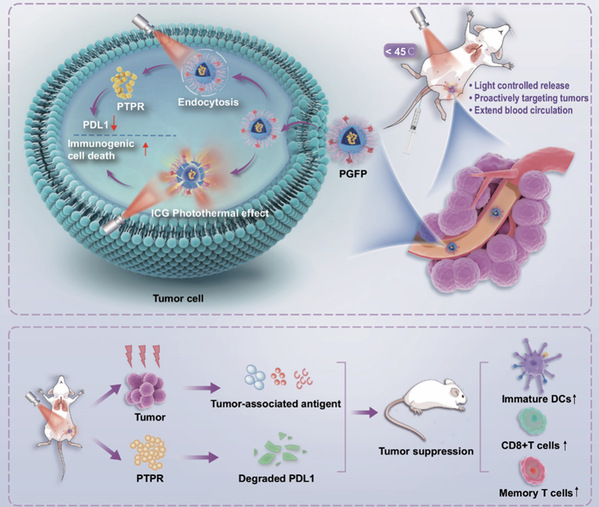
This study developed a multifunctional biomimetic nano-peptide drug delivery system named PGFP+, which integrates three core modules: 1) a fluorinated PD-L1 inhibitory peptide (PTPR) with enhanced stability and intracellular delivery efficiency; 2) the photosensitizer indocyanine green (ICG), which—under near-infrared irradiation—triggers a liposomal phase transition to facilitate drug release and induces immunogenic cell death via mild photothermal effects (42°C), thereby activating a systemic immune response; and 3) a platelet membrane coating that prolongs circulation, evades immune clearance, and enables precise targeting via CD62p/CD44 interactions.
In triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) models—including orthotopic, distant, and metastatic tumors—PGFP+ effectively suppressed tumor progression, enhanced T-cell infiltration, promoted dendritic cell maturation, downregulated PD-L1 expression in the tumor microenvironment, and induced durable immune memory, thereby preventing recurrence. The mild photothermal therapy avoided high-temperature damage, while the platelet membrane camouflage minimized off-target side effects, collectively improving treatment safety.
This work proposes an integrated “precision delivery + immune activation” strategy for peptide-based drugs, offering a new approach to enhance the stability, tumor targeting, and delivery efficiency of immunomodulatory peptides. It also provides a promising therapeutic option for refractory tumors such as TNBC.
Link: https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202506841