Title: Core Fucosylation Represses SMURF1-Dependent Degradation of CD47 to Promote Tumor Immune Evasion
Yuting Cao , Siyuan Chai , Mingyang Li , Xiaoming Chen , Jiating Hu , Bingyi Lin , Liming Wu , Wen Yi, Qiang Zhu
Abstract
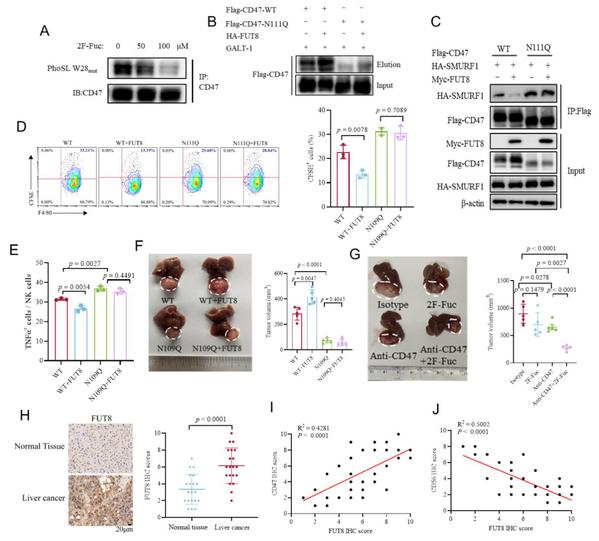
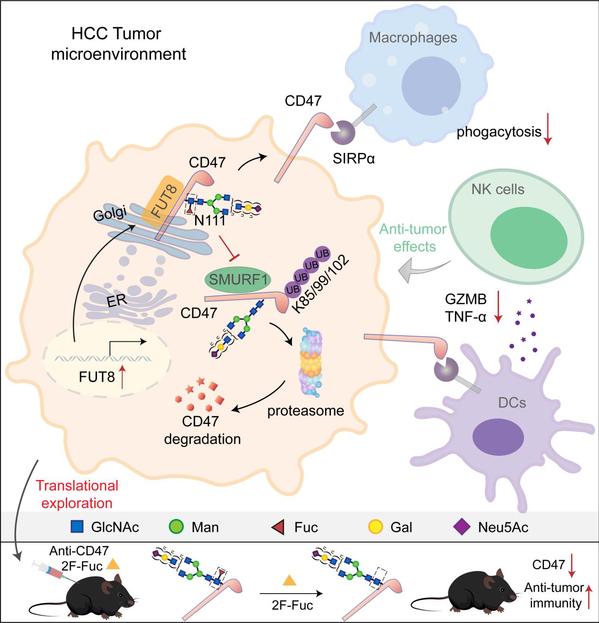
Glycosylation, the covalent attachment of glycans to proteins, lipids, and RNAs, is fundamental in regulating diverse biological processes. Glycosylation patterns are aberrantly altered in the tumor microenvironment and closely associated with tumor immune escape. However, the molecular mechanisms by which glycosylation regulates tumor immune escape are poorly understood. We show that Cluster of Differentiation 47 (CD47), an innate immune checkpoint protein, is highly modified with core fucosylated N-linked glycans. Core fucosylation of CD47 mediated by fucosyltransferase 8 (FUT8) at asparagine 111 (N111) reduces CD47 ubiquitination and degradation. Blockade of N111 glycosylation represses CD47 expression and promotes macrophage phagocytosis of tumor cells. Furthermore, elimination of N111 glycosylation promotes the infiltration of CD103+ dendritic cells (DCs), leading to the increased recruitment of natural killer (NK) cells and inhibition of tumor growth in a murine hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) model. Combined treatment with core fucosylation inhibitors and an anti-CD47 antibody synergistically promotes therapeutic efficacy in the HCC model. Finally, FUT8 levels in human HCC specimens are positively correlated with CD47 expressions and negatively correlated with the infiltration of CD103+ DC and NK cells. Collectively, this study reveals a mechanism underlying CD47 upregulation in tumor cells and highlights the potential of targeting the FUT8-SMURF1-CD47 axis as a therapeutic strategy to improve anti-tumor immune responses.
Link: http://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202516863