Title:RBOHC-derived ROS control plant nitrate starvation response via WRKYs-activated expression of high-affinity nitrate transporters
Tian Yuan , Meng-Qi Cui , Chen Xu , Jing-Ying Yan , Wo-Na Ding , Ji-Ming Xu , Yun-Rong Wu , GuiXin Li , Yu Liu , Dong Zhang , ChuanZao Mao , Moussa Benhamed , Chong-Wei Jin , Zhong-Jie Ding , Shao-Jian Zheng
Abstract
Nitrogen is a fundamental element in the life of plants. In dryland soils, nitrate nitrogen is the main form of nitrogen absorbed by plants, but its content exhibits significant spatial and temporal heterogeneity in farmland soils. Facing environments where nitrate nitrogen is sometimes abundant and sometimes scarce, plants have evolved a sophisticated regulatory system. However, compared with the primary nitrogen response mechanisms under nitrogen-sufficient conditions that have been extensively studied, there are still many unknowns about how plants quickly adjust growth and efficiently acquire nitrogen sources under nitrogen starvation stress.
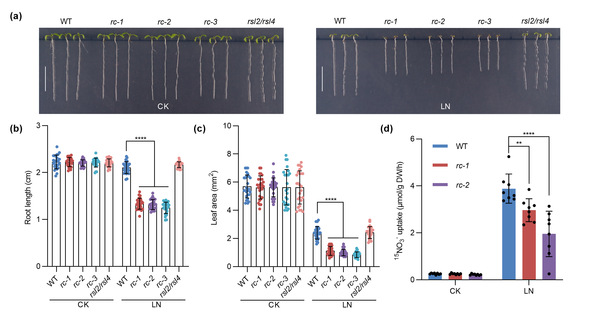
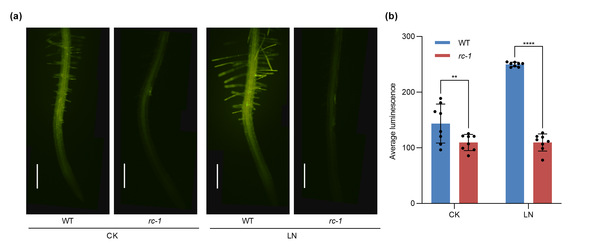
The research team discovered through systematic genetic screening that the loss-of-function mutant of the RBOHC gene in Arabidopsis (rbohc, rc-1) exhibits growth-inhibited phenotypes under low nitrogen conditions, such as shortened root length and reduced leaf area, along with decreased nitrate uptake capacity. These phenomena do not occur under nitrogen-sufficient conditions , indicating that RBOHC is a plant-specific positive regulator in response to nitrogen starvation.
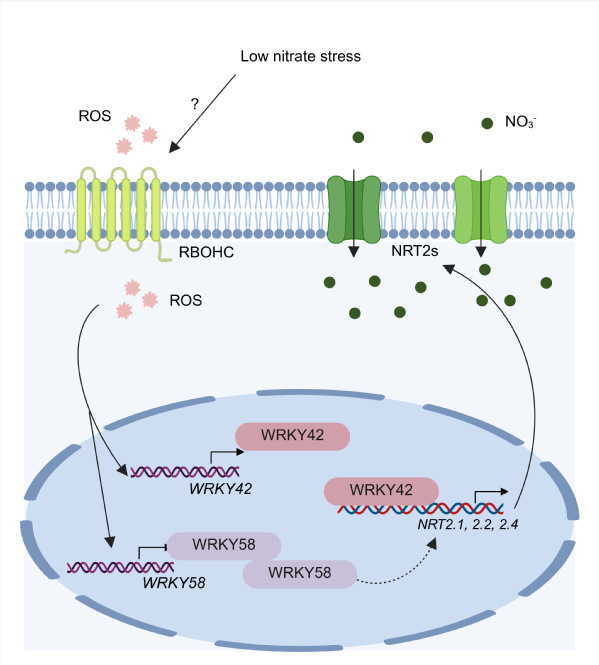
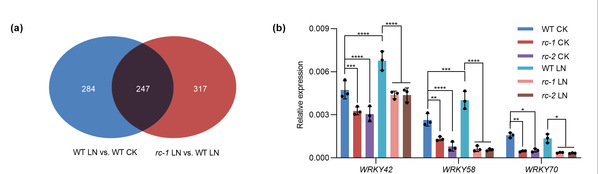
This study established the 'RBOHC–ROS–WRKY–NRT2' signaling pathway framework in Arabidopsis for the first time, revealing the positive regulatory role of ROS in nitrogen starvation responses and expanding the research dimension of the cross-regulation between plant nutrient signals and oxidative signals. In the future, in-depth studies on the post-translational regulatory mechanisms of RBOHC in this pathway and how ROS precisely regulates WRKY transcriptional activity are expected to provide new molecular targets and breeding strategies for the genetic improvement of crop nitrogen use efficiency, contributing to the development of green and sustainable agriculture.
Link:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095927325012654