Title: Distribution of N and recently fixed C among a common mycorrhizal network linking an invasive plant, Solidago canadensis, and a native plant, Kummerowia striata
Awagul Awaydul, Jing Xiao, Xin Chen, Roger Koide, Yongge Yuan, Lei Cheng
Abstract
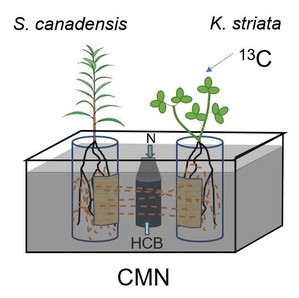
1. The invasive plant species, Solidago canadensis, often shares a common mycorrhizal network (CMN) with native plant species in southeast China. We ask whether the transfer of carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) among the invasive S. canadensis, the native Kummerowia striata and their CMN could contribute to the invasiveness of S. canadensis.
2. We conducted a microcosm experiment in which a CMN was established on S. canadensis and K. striata. We used 13CO2 pulse-labelling to quantify the relative contribution of recently fixed C from the two host species to the CMN. We also calculated the relative N distribution to each host species from the CMN.
3. We found that 89% of the recently fixed C in the CMN originated from S. canadensis, while 11% originated from K. striata. We also found that the CMN distributed 77% of the N it absorbed to S. canadensis and 23% to K. striata.
4. Our results suggest that the unequal distribution of N from a CMN to the invasive and native plant species is related to the unequal contribution of C from the plant species. This mechanism could contribute to invasion of native communities by alien species when there is a stoichiometric exchange of limiting nutrients for C, and when alien species contribute more C to the CMN than natives.
Link: http://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.14392